Flip-Flop (SR, JK, D, T) Truth Table Generator
Select flip-flop type and inputs to see the corresponding outputs.
Welcome to the Flip-Flop Truth Table Generator on our site truth table generator, your comprehensive tool for understanding and analyzing the behavior of fundamental flip-flop circuits in digital electronics. Access our online platform for interactive tools to learn, practice, and master logic and discrete math concepts.
What is a Flip-Flop?
A flip-flop is a basic memory element in digital electronics, capable of storing a single bit of data. It has two stable states and can change states based on input signals, making it essential for memory storage, data transfer, and timing applications. The primary types of flip-flops include:
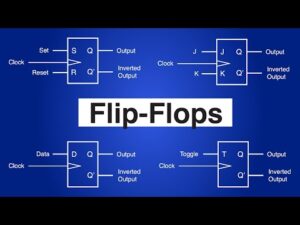
• SR (Set-Reset) Flip-Flop: Controls the state using set and reset inputs.
• JK Flip-Flop: An enhancement over SR flip-flop, eliminating invalid states.
• D (Data or Delay) Flip-Flop: Captures the value of the data input on a clock edge.
• T (Toggle) Flip-Flop: Toggles its state on each clock pulse when the toggle input is high.
How to Use the Flip-Flop Truth Table Generator
1. Select Flip-Flop Type: Choose from SR, JK, D, or T flip-flop.
2. Input Parameters: Enter the current state and input values.
3. Generate Table: Click on “Generate” to view the truth table.
4. Analyze Results: Study the output states corresponding to different input combinations.
Flip-Flop Truth Tables
SR (Set-Reset) Flip-Flop
| S | R | Q (Next State) | Description |
| 0 | 0 | Q (No Change) | Hold State |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Reset |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Set |
| 1 | 1 | Undefined | Invalid State |
JK Flip-Flop
| J | K | Q (Next State) | Description |
| 0 | 0 | Q (No Change) | Hold State |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Reset |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Set |
| 1 | 1 | Q’ (Toggle) | Toggle State |
D (Data) Flip-Flop
| D | CLK | Q (Next State) | Description |
| 0 | ↑ | 0 | Reset |
| 1 | ↑ | 1 | Set |
| X | 0 | Q (No Change) | Hold State |
T (Toggle) Flip-Flop
| T | CLK | Q (Next State) | Description |
| 0 | ↑ | Q (No Change) | Hold State |
| 1 | ↑ | Q’ (Toggle) | Toggle State |
Applications of Flip-Flops
• Memory Storage: Used in registers and memory devices to store binary data.
• Counters: Implementing binary and decade counters.
• Frequency Division: Dividing clock signals in timing applications.
• Data Transfer: Synchronizing data between different parts of a system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main difference between SR and JK flip-flops?
The SR flip-flop has an undefined state when both inputs are high, whereas the JK flip-flop resolves this by toggling the output, eliminating the invalid state.
How does a D flip-flop differ from other types?
The D flip-flop captures the value of the data input at a specific clock edge, ensuring that the output changes only at that moment, making it ideal for data storage.
When should I use a T flip-flop?
T flip-flops are best used in applications requiring toggling behavior, such as in counters and frequency dividers.
Can I simulate these flip-flops using this tool?
Yes, the Flip-Flop Truth Table Generator allows you to input different scenarios and observe the resulting state transitions, aiding in understanding and design.
